Thursday, May 23, 2019
Friday, May 17, 2019
Thursday, May 16, 2019
Semiotics Theory
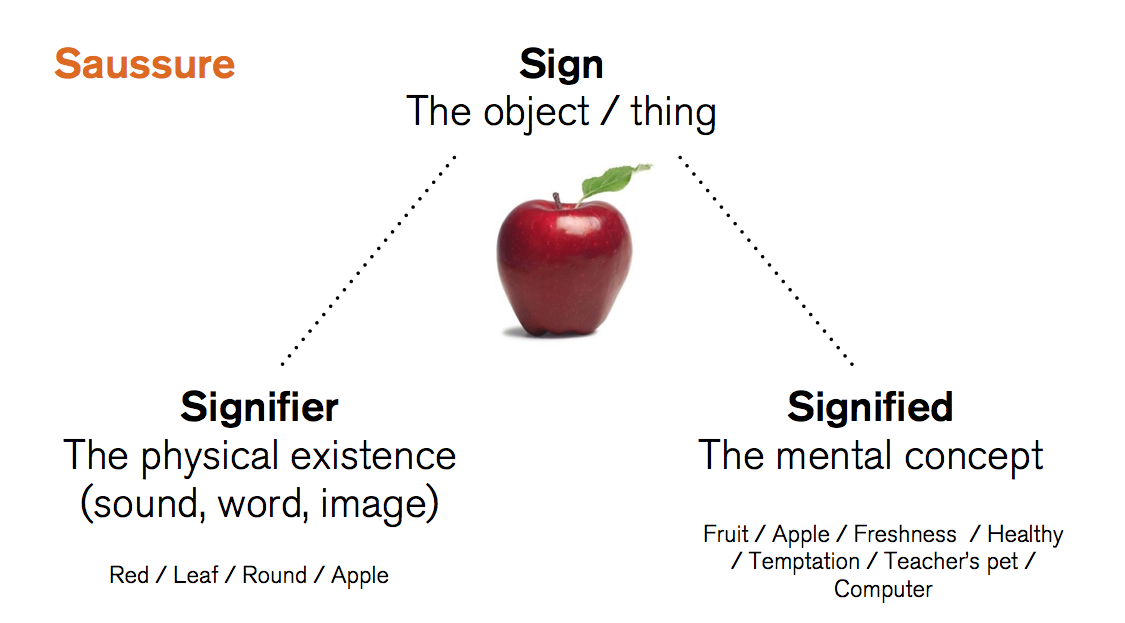
Ferdinand de Saussure was a Swiss academic who developed theory in semiotics (the study of signs and symbols and their interpretations). He argued that there were 2 inseparable elements to every sign; the signifier and the signified. We can apply this basic theory to our analysis of texts by considering what meaning is signified by the existence of a signifier. For example:
The representation that is offered to the audience depicts her as attractive, with striking blonde hair, she is made-up with provocatively bright red lipstick which signifies femininity, fashion and beauty.
In this instance the signifier is the blonde hair and red lipstick and the signified is the mental concept or meaning created by it.
It works in a similar way to the use of denotation and connotation that was developed by Roland Barthes. Signs convey meaning and this can be decoded by denoting what it is and connoting the associated meaning that is conveyed to an audience. For example:
Her mouth is open overtly and it exaggerates the denotation of the bright red colour of the lipstick. The red is used with pink throughout the advert and suggests traditional connotations of femininity, love and passion.
Uses and Gratifications Theory
Uses and Gratifications theory was developed by Blumler and Katz suggests that media users as an audience play an active role in choosing and consuming media products to satisfy specific needs.
Blumler and Katz believed that the user (audience) seeks out the media source that best fulfills their needs.
Blumler and Katz believed that the user (audience) seeks out the media source that best fulfills their needs.
The uses and gratifications theory assumes the audience chooses what media products it wants to consume for four different needs:
1 The need for information and education – the audience want to acquire information, knowledge and understanding by watching programmes like the news or documentaries or reading newspapers.
2 The need for personal identity - the audience can recognise a person or a product, role models that reflect similar values to themselves and mimic or copy some of their characteristics.
3 The need for integration and social interaction – the ability for a media product to produce a topic of conversation between people who consume it. For example who is the best contestant on The X-factor, the best couple on Love Island or what was the best goal shown on Match of the Day.
4 Escapism, diversion or entertainment– computer games and action films let viewers escape their real lives and imagine themselves in those situations. Audiences seeking enjoyment from media products.
The videos below explain Blumler and Katz's Uses and Gratifications theory and provide some examples to look at for your exam.Tuesday, May 7, 2019
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
http://www.thisgirlcan.co.uk/ https://the-dots.com/projects/this-girl-can-case-study-142741